[OODP] 10. Class Inheritance
POSTECH OODP Lecture at 24SS
Class Inheritance
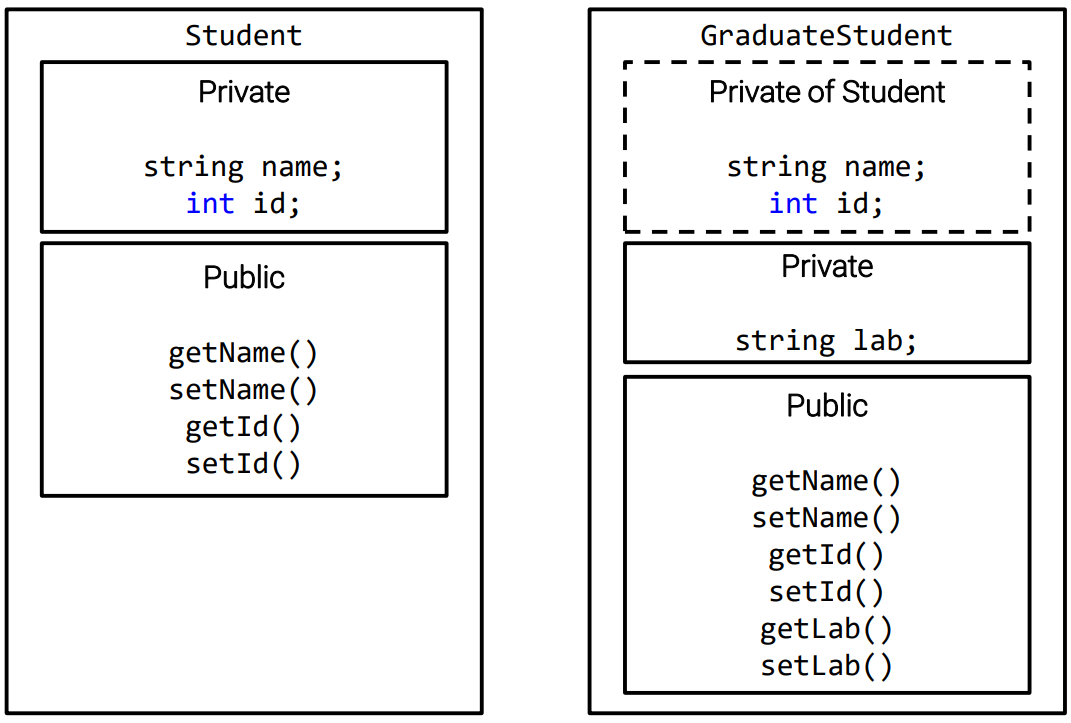
Class 상속은 높은 코드 재사용성을 제공한다. 상속하도록 설계된 base class와 상속 받는 derived class로 구성된다. 간단한 base class의 예시는 다음과 같다.
class Student
{
private:
string name;
int id;
public:
Student(const string &name_ = "", int id_ = 0);
void setName(const string &name_) { name = name_; }
const string& getName() const { return name; }
void setId(int id_) { id = id_; }
int getId() const { return id; }
};
Student::Student(const string &name_, int id_)
: name(name_), id(id_)
{ }
학생이라는 커다란 분류 아래, 대학원생들을 표현하는 deriving class의 간단한 예시는 다음과 같다.
class GraduateStudent : public Student
{
private:
// string name; int id;
string lab;
public:
GraduateStudent(const string &name_ = "", int id_ = 0, const string &lab_ = "");
// void setName(const string &name_) { name = name_; }
// const string& getName() const { return name; }
// void setId(int id_) { id = id_; }
// int getId() const { return id; }
void setLab(const string &lab_) { lab = lab_; }
const string& getLab() const { return lab; }
};
GraudateStudent::GraudateStudent(const string &name_, int id_, const string &lab_)
// : name(name_), id(id_), lab(lab_)
: Student(name_, id_), lab(lab_)
{ }
주석은 상속 받지 않았을 때 필요한 member들이다. : public Student 구문을 통해 Student의 public member들을 GraduateStudent 자신의 interface처럼 사용할 수 있다. 한편, Student의 private member들은 GraduateStudent가 사용할 수 있지만 GraduateStudent의 member function으로 직접 제어할 수는 없다. name과 id를 = 연산자로 할당하지 않고, initializer list로 초기화하는 이유이다.
상속되지 않는 member들도 존재하는데, constructor&destructor와 assignment operator들이 그것이다. 이는 derived class가 base class에 비해 data member들이 추가되는 경우가 잦아, 자체적으로 정의하는 것이 자연스럽기 때문이다.
Speicial Relationships Btw. Derived & Base Classes
- derived-class object는 base-class의 public method들을 사용할 수 있다.
GraduateStudent st2("Yeri", 20052465, "Computer Graphics Lab");
cout << st2.getName() << ", " << st2.getId() << " , ";
- base-class pointer와 reference는 derived-class 객체를 explicit typecast 없이 지칭할 수 있다. 이를 upcasting이라고 부른다.
GraduateStudent st2("Yeri", 20052465, "Computer Graphics Lab");
Student *pt = &st2;
cout << pt->getName() << ", " << pt->getId() << endl;
Student &ref = st2;
cout << ref.getName() << ", " << ref.getId() << endl;
그러나 base-class pointer or reference로 derived-class method를 호출하는 것은 불가능하다.
cout << pt->getLab() << endl; // NOT ALLOWED
cout << ref.getLab() << endl; // NOT ALLOWED
반대로, explicit typecast 없이 derived-class pointer나 reference로 base-class 객체를 활용하는 downcasting은 허용되지 않는다.
Student st1("Irene", 20011110);
GraduateStudent *pp = &st1; // NOT ALLOWED
GraduateStudent &rr = st1; // NOT ALLOWED
이렇게 Public inheritance가 가능한 관계를 is-a relationship이라고 부른다(“GraduateStudent is a Student”). derived class의 객체는 base class의 객체이기도 하기 때문이다.
Polymorphic Public Inheritance
base-class에 새로운 속성을 추가했을 뿐인 is-a와 달리, base class에서 다소 변경을 주는 has-a relationship가 존재한다(“Lunch has a Fruit”).
Student st1("Irene", 20011110);
GraduateStudent st2("Yeri", 20052465, "Computer Graphics Lab");
st1.display(); // displays name & id
st2.display(); // displays name, id & lab
이러한 다형성 상속의 핵심은 virtual method의 overloading과 overriding이다.
Name Hiding in Inheritance
void Student::reset(const string &name_, int id_);
void GraduateStudent::reset(const string &name_, int id_, const string &lab_);
GraduateStudent st2("Yeri", 20052465, "Computer Graphics Lab");
st2.reset("Hojin", 20031212, "SE Lab"); // OK
st2.reset("Chulhoon", 20052323); // error!
st2.Student::reset("Chulhoon", 20052323); // OK
위와 같이 동일한 이름을 가진 inherited member는 local member에 의해 가려질 수 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해서는 다음과 같이 수정할 수 있다.
void GraduateStudent::reset(const string &name_, int id_, const string &lab_=“”)
void GraduateStudent::reset(const string &name_, int id_) { Student::reset(name_, id_); }
virtual Keyword
virtual 예약어가 붙은 method는 컴파일러에게 override될 것을 알린다.
Student *ptr[2];
ptr[0] = new Student("Irene", 2001110);
ptr[1] = new GraduateStudent("Yeri", 20052465, "Computer Graphics Lab");
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
ptr[i]->display();
위의 코드에서 virtual로 display()를 선언하지 않았다면, ptr[1]은 Student 객체만을 가리킬 수 있기 때문에 GraduateStudent::display가 아니라 Student::display()를 호출하게 된다. 그러나 virtual method로 선언을 한다면, Student 타입의 포인터가 GraduateStudent 타입의 객체의 method를 호출할 수 있다.
결론적으로, Polymorphism을 통해 base class의 포인터가 다양한 타입의 객체를 가리킬 수 있고, 각 객체들은 실제 타입에 따라 다르게 동작할 수 있다.
Function Binding
- overloading된 함수들 중 무엇을 호출해야하는지 결정하는 작업이다.
- Static binding : 일반적인 함수들을 대상으로 컴파일타임에 수행된다.
- Dynamic binding : virtual function들에 대하여 런타임에 수행된다. 자연히, 실행속도도 느려진다.
- 그렇다면 어떻게 compiler가 virtual function들을 관리할 수 있을까?
각 객체마다 vptr라는 hidden member가 생성된다. vptr은 vtable을 가리키는데, vtable은 virtual function들의 주소를 저장하는 배열이다. 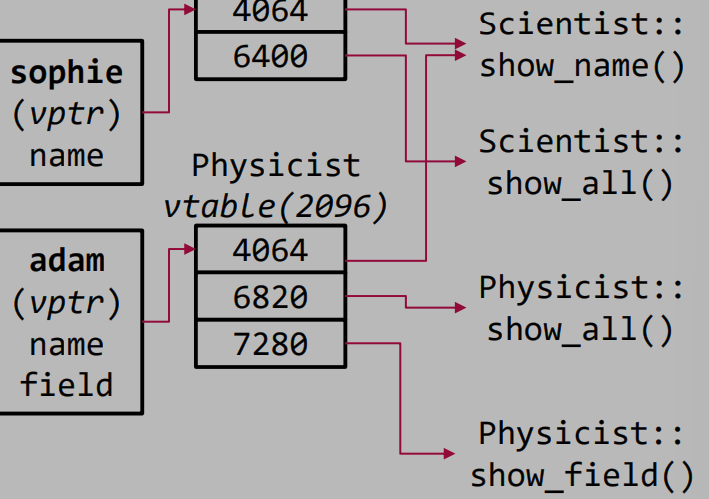 아래 코드 예시에서 위와 같이 vtable이 생성된다.
아래 코드 예시에서 위와 같이 vtable이 생성된다.
class Scientist {
// ...
char name[40];
public:
virtual void show_name();
virtual void show_all();
// ...
};
class Physicist : public Scientist {
// ...
char field[40];
public:
void show_all(); // redefined
virtual void show_field(); // new
// ...
};
Scientist sophie("Sophie");
Physicist adam("Adam", "nuclear");
Scientist *psc = &adam;
psc->show_all();
Things to know about virtual method
- constructor는 virtual로 선언될 필요가 없다.
- class에 virtual method가 있다면 virtual destructor를 정의해라.
- 상속에서 pointer나 reference를 쓴다면 virtual destructor를 정의하라.
Access Control
public과 private과 같은 접근제어자에는 protected도 포함되어 있다. protected member의 경우에는 class 외부에서는 접근할 수 없지만, derived class에서는 접근할 수 있다.
Abstract Base Classes
Pure virtual functions를 가진 base class를 일컫는다. Abstract base class로는 객체를 만들 수 없다. 오직 base class로써만 기능한다.
class Shape { // abstract base class
// ...
virtual double Area() const = 0; // a pure virtual function
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
// ...
double Area() const { return 3.141592 * radius * radius; }
};
class Rectangle : public Shape
{
// ...
double Area() const { return width * height; }
};
Pure virtual function은 정의되지 않은 함수이다. 따라서 반드시 derived class에서 재정의되어야 한다. base class에서는 “=0”으로 확인할 수 있다.
Questions?
Q1. “void display() const;” 이 구문에서 const는 어떤 역할을 하나요?
A1. 주어진 메소드에서 어떠한 member data 변경도 없을 것을 알려준다. read-only 라는 뜻이다.
Q2. virtual이 실행속도도 낮고, 복잡하게 만드는 원인 같은데 꼭 써야하는 이유가 있나요?
A2. 코드 가독성(?) 때문이다. virtual이라는 키워드는 곧 derived class에서 재정의될 수 있다는 것을 의미한다. 반대로 virtual이 없다면, derived에서 재정의하지 않을 것이라는 의미를 암묵적으로 가진다. 개발자가 이해하기 쉽도록 만들어졌다.
Q3. 만약 base class에서 선언한 member data를 derived class에서 재정의하고 싶다면 어떻게 해야하나요? 예를 들어, name[5]를 name[40]으로 바꾸려면 어떻게 해야할까요? A3.
[students]:
