Standard Template Library(STL)
Iterators
structure에 관계 없이 동일한 동작의 코드를 구현할 수 있도록 돕는다.
구현하려는 알고리즘에 따라서 iterator에 요구하는 연산자가 다른다. 예를 들어 find의 경우, 읽을 수만 있으면 되기에 ++ 연산자로 충분하다. sort의 경우에는 임의의 위치로 읽고 쓸 수 있어야하기에 + 연산자가 필요하다. 따라서 STL은 5종류의 iterator을 정의한다. 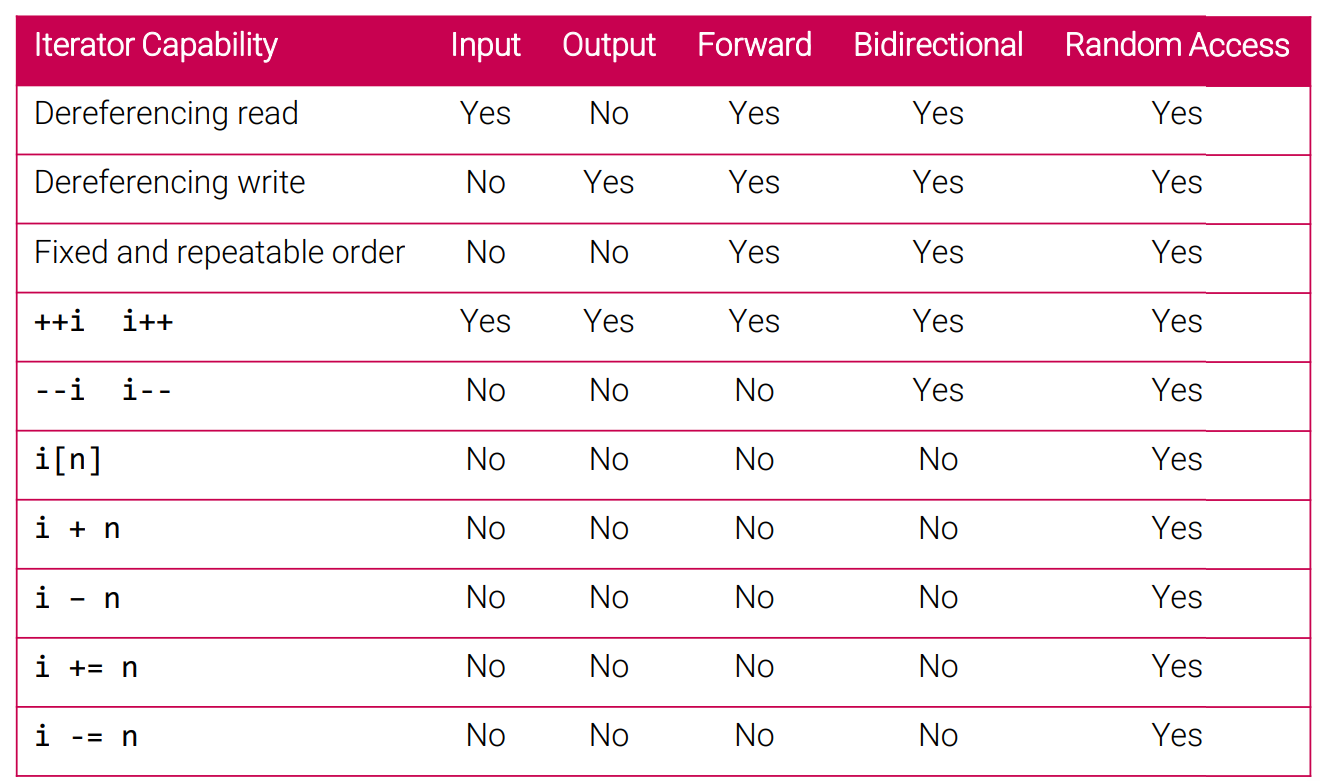
Container
Container란 다른 객체나 타입들을 저장할 수 있는 객체이다. STL에는 크게 세가지 종류의 container가 존재한다.
- container
- sequence container : vector, array, stack, queue, deque, priority_queue, list, forward_list
- associative container : set, multiset, map, multimap
Associative container는 key와 값을 묶어 Tree 구조로 저장한다. 한편, unordered associative container는 hash table 구조로 구현되어 있다.
Function Objects(functors)
마치 함수처럼 괄호 연산자 ‘()’를 사용할 수 있는 객체를 functor라고 부른다.
class Functor {
public:
double operator() (double x) { return x * 2.0; }
};
Functor f;
double y = f(5.0); // equivalent as f.operator() (5.0);
또한 STL 함수들은 functor를 argument로 받을 수도 있다.
bool tooBig(int n) { return n > 100; }
list<int> scores;
scores.remove_if(tooBig);
// maybe
void list::remove_if(functor?) {
for (int n : this) {
if (functor(n))
this.remove(n);
}
}
// make toobig as class
template<class T>
class TooBig {
private:
T cutoff;
public:
TooBig(const T& t) : cutoff(t) {}
bool operator() (const T& v) { return v > cutoff; }
};
list<int> scores;
scores.remove_if(TooBig<int>(200));
위의 코드는 [tooBig.cpp]에서 완성해보겠다.
STL Algorithms
initializer_list Template
Questions?
Q1.
A1.
Q2.
A2.
[functor.cpp]: [tooBig.cpp]:
