[OODP] 0. About C++(1)
POSTECH OODP Lecture at 24SS
오랫동안 Java를 다뤄왔지만 객체지향설계에 대해 올바르게 이해하고 있는지에 대한 의구심은 항상 마음속에 있었다. 한편, 가장 완벽에 가까운 언어인 C와 그 계열 언어에 대한 자신감도 부족했다. 따라서 졸업 전, 마지막 학기 동안 C++로 객체지향설계패턴을 조성현 교수님께 듣고자 한다. 먼저 C++에 대해서 간단히 정리하고 넘어가겠다.
C++ Language’s three category
C++은 C 언어를 기반으로 Object-oriented programming과 Generic Programming을 지원한다. 따라서 C++은 다음의 세가지 programming 카테고리에 들어간다.
- Procedure Language : C에 의한 절차지향 언어
- Object-oriented Language : C++의 class에 의한 객체지향 언어
- Generic Programming : C++ templates로 지원되는 생성형 언어
이 세가지 관점에서 어떻게, 무엇을 목적으로 기능하는지 살펴보겠다.
Procedure Language
- Assembly 언어
(almost)one-to-one traslation between machine instructions and human-readable keywordspushq %rbp .seh_pushreg %rbp movq %rsp, %rbp .seh_setframe %rbp, 0 .seh_endprologue movss %xmm0, 16(%rbp) movss %xmm1, 24(%rbp) movss %xmm2, 32(%rbp) movss %xmm3, 40(%rbp) movss 16(%rbp), %xmm0 addss 32(%rbp), %xmm0 movq 48(%rbp), %rax movss %xmm0, (%rax) movss 24(%rbp), %xmm0 addss 40(%rbp), %xmm0 movq 56(%rbp), %rax movss %xmm0, (%rax) nop popq %rbp ret - Earlier Procedure Languages
Ex) Basic, Fortran, …
Spaghetti programming의 위험이 있다 : Organizational problems as programs grew larger. 특히 “goto” 같은 statement를 사용할 경우 더욱 그렇다.10 PRINT "Complex Number Calculator" 20 INPUT "What operation do you want to compute? ", OP$ 30 IF OP$ = "+" OR OP$ = "-" OR OP$ = "*" OR OP$ ="/" THEN GOTO 100 40 IF OP$ = "EXIT" THEN END 50 PRINT "Not supported operation!" 60 GOTO 20 100 INPUT "Input the first number (real, imaginary) ", R1, I1 110 INPUT "Input the second number (real, imaginary) ", R2, I2 120 IF OP$ = "+" THEN GOTO 200 130 IF OP$ = "-" THEN GOTO 300 140 IF OP$ = "*" THEN GOTO 400 150 IF OP$ = "/" THEN GOTO 500 200 R3 = R1 + R2 210 I3 = I1 + I2 220 PRINT "(";R1;"+";I1;"i) + (";R2;"+";I2;"i) = ";R3;"+";I3;"i" 230 GOTO 20 300 R3 = R1 - R2 310 I3 = I1 - I2 320 PRINT "(";R1;"+";I1;"i) - (";R2;"+";I2;"i) = ";R3;"+";I3;"i" 330 GOTO 20 400 R3 = R1*R2 - I1*I2 410 I3 = R1*I2 + R2*I1 420 PRINT "(";R1;"+";I1;"i) * (";R2;"+";I2;"i) = ";R3;"+";I3;"i" 430 GOTO 20 500 DENOM = R2*R2 + I2*I2 510 R3 = (R1*R2 + I1*I2) / DENOM 520 I3 = (-R1*I2 + R2*I1) / DENOM 530 PRINT "(";R1;"+";I1;"i) / (";R2;"+";I2;"i) = ";R3;"+";I3;"i" 540 GOTO 20점차 구조화 되어 Structured Programming이 나타났다. Top-down 설계를 통해 커다란 프로그램을 좀 더 작은 일들로 세분화한다. 또한 fuction으로 모듈화할 수 있다.
- C 언어
Unix 운영체제를 개발하기 위해 만들어진 언어다. cocisne(간결)하고, compact(작고) and fast(빠른) 프로그램을 생성하며, 하드웨어를 효율적으로 제어할 수 있는 high-level 프로그래밍 언어가 필요로 했다.
Object-Oriented Programming
Procedural language가 algorithm에 집중했다면, OOP는 data를 강조한다. 문제에 필요한 형태로 다음과 같이 data를 설계한다.
- Class : Specification describing such a new data form
- 객체를 나타내는 데 사용되는 data
- 해당 data에 대해 수행할 수 있는 operation
- Object : class에 따라 구성된 data structure
OOP에서는 큰 프로그램이 다뤄야할 것들을 정확히 표현해내는 class를 설계한 후, 이들의 object를 사용하여 프로그램을 구성하는 bottom-up programming의 방식을 따른다. 따라서 OOP는 1) software를 이해하고 조직하기 용이하여, 2) 개발 및 유지보수 비용(cost)이 감소하고, 3) software components들을 재사용(reuse)하기 쉽다는 장점이 있다.
- Abstract Data Type : A data type in which only high-level operations are exposed as public interfaces while low-level datails are hidden
C++에서 ADT는 class를 통해 구현된다. ADT(즉, class)의 특징은 information hiding과 encapsulation이다. C++은 public interface와 private implementation details, private datas 등을 통해 접근 범위를 제어한다. 이러한 구조는 사용자에게 추상화된 interface를 제공하여, object를 사용하는 데 있어서 세부 구현 사항을 숨길 수 있다. 물론, procedural language에서도 ADT 구조를 구현할 수 있다. C의 struct(구조체)가 그 예이다.
Generic Programming
OOP와 마찬가지로 코드의 재사용성과 일반적인 개념을 추상화하는 기법이다. data 측면을 강조하는 OOP와 함께 제공되지만, Generic Programming은 특정한 data type에 독립적인 코드를 생성하는 데 중점을 둔다. OOP가 큰 프로젝트를 관리하는 도구로 사용된다면, Generic Programming은 data sorting이나 list merging과 같은 일반적인 작업을 수행하는 도구를 제공한다.
“Generic” refers to code that is type independent
C++에는 integer, characters, floating-point numbers, strings of characters 와 같은 수많은 data type들이 존재한다. Generic Programming은 generic tpye의 함수 하나로, 다양한 실제 type들에 대해 사용할 수 있도록 한다. 이는 C++ template을 통해 제공된다.
C++에서 동일한 기능을 Structured Programming부터 OOP Programing, Generic Programming으로 구현한 코드를 보고 싶다면 complex_calculator예제를 참고해도 좋겠다.
The Genesis of C++
C++은 C의 superset(초집합, 포함집합)이다. C의 brevity(간결성), suitability to system programming, widespread availability, 그리고 Unix 운영체제와의 긴밀한 연결성을 살리기 위해 이를 기반으로 하였다. C의 구성요소들을 크게 수정하지 않고 OOP feature과 generic programming support만을 더했다.
The Standard:Standard C++(isocpp.org)
Mechanics of Creating a Program
C++로 프로그램을 작성했을 때, 어떻게 동작하는가?
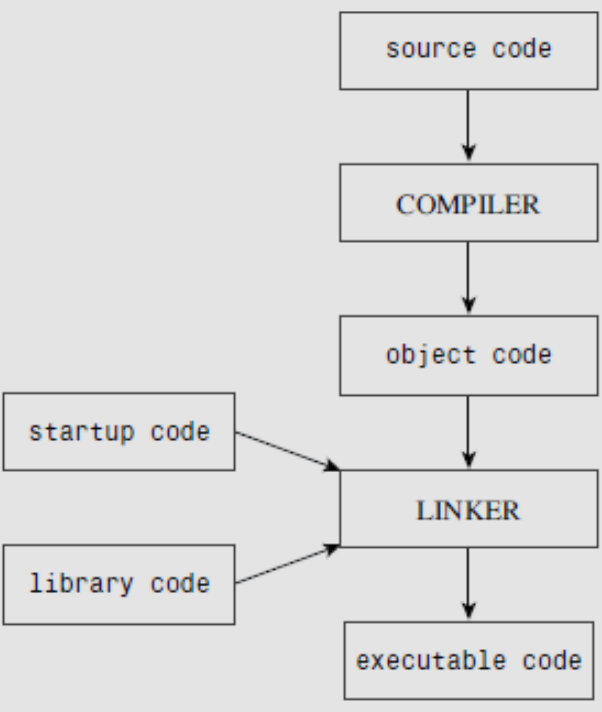
- Steps
- Write source code and save in a file
- Compile(translate) the source code to the object code which containing the machine language used by the host computer
- Link the object code with additional code, then get an executable code.
- File Extensions
- .c : C source code
- .h : C header file
- cc, cxx, cpp, c++ : C++ source code
- h, hh, hxx, hpp : C++ header file
- C++ Compiler
- Microsoft Visual C++
- g++ : A part of GNU compiler. Available on various platforms.
- C++ IDE : provides a collection of tools including an editor, compiler, linker, debugger.
- Microsoft Visual Studio Visual Studio 2022
- Visual Studio Code : A cross-platform editor which provides a number of plugins.
- Compiling a C++ Program
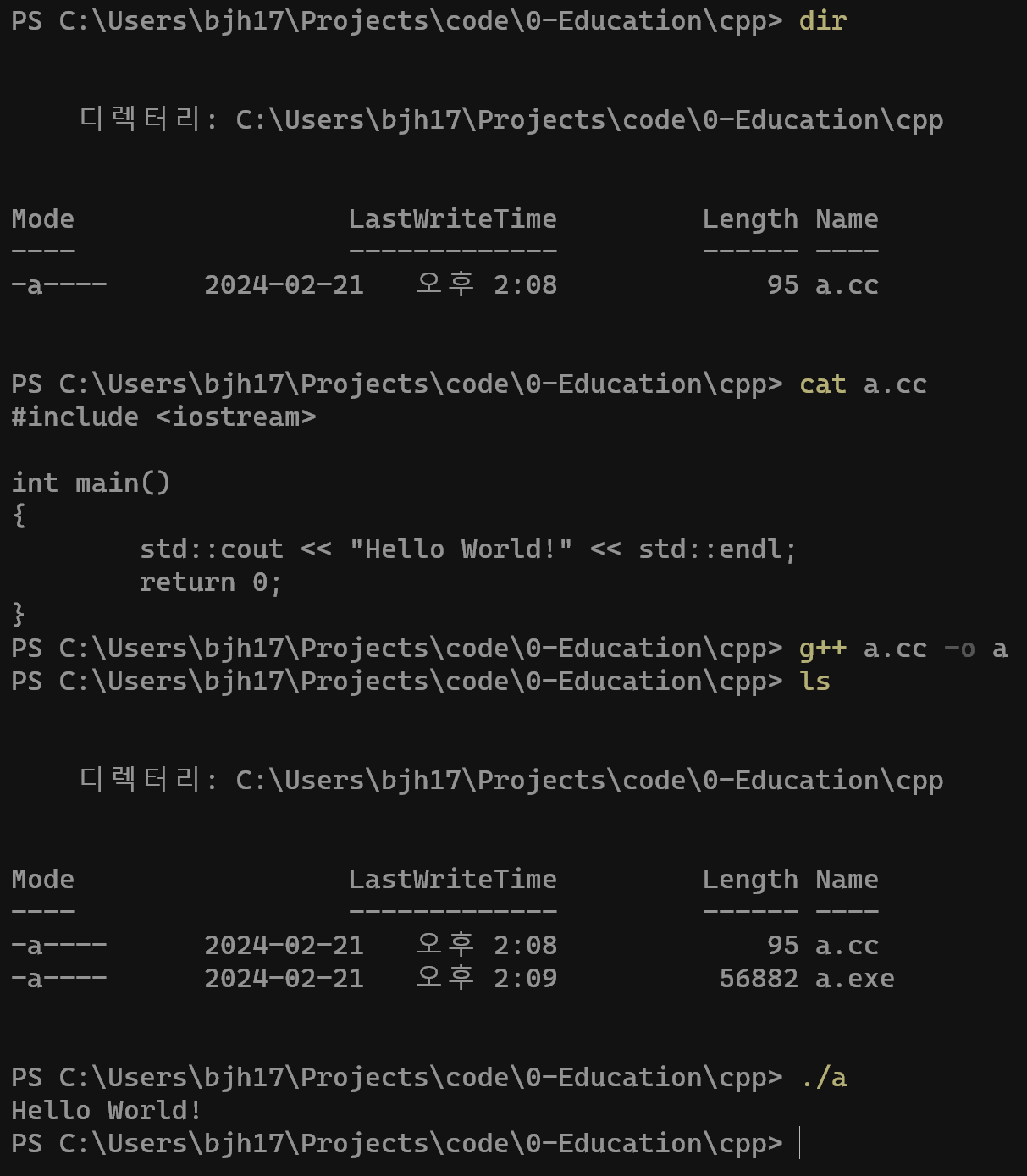
- Compiles and links the code
- Get executable files
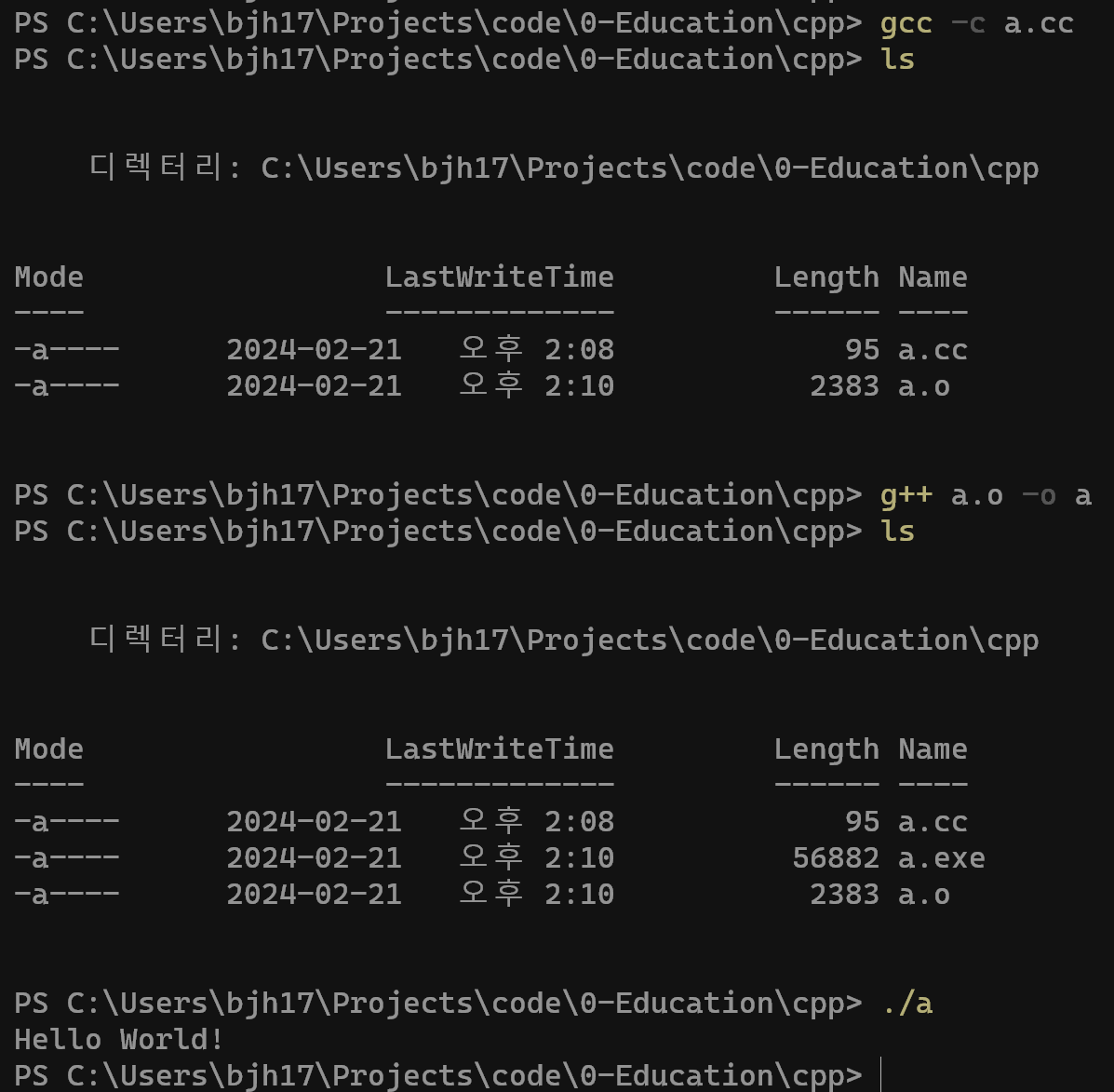
- -c : compilation only, then get an object file
- Linking only, then get an executable file
조금 더 자세한 내용을 원한다면 다음 설명을 참고해도 좋을 것 같다.
